Monocot Stem Labeled
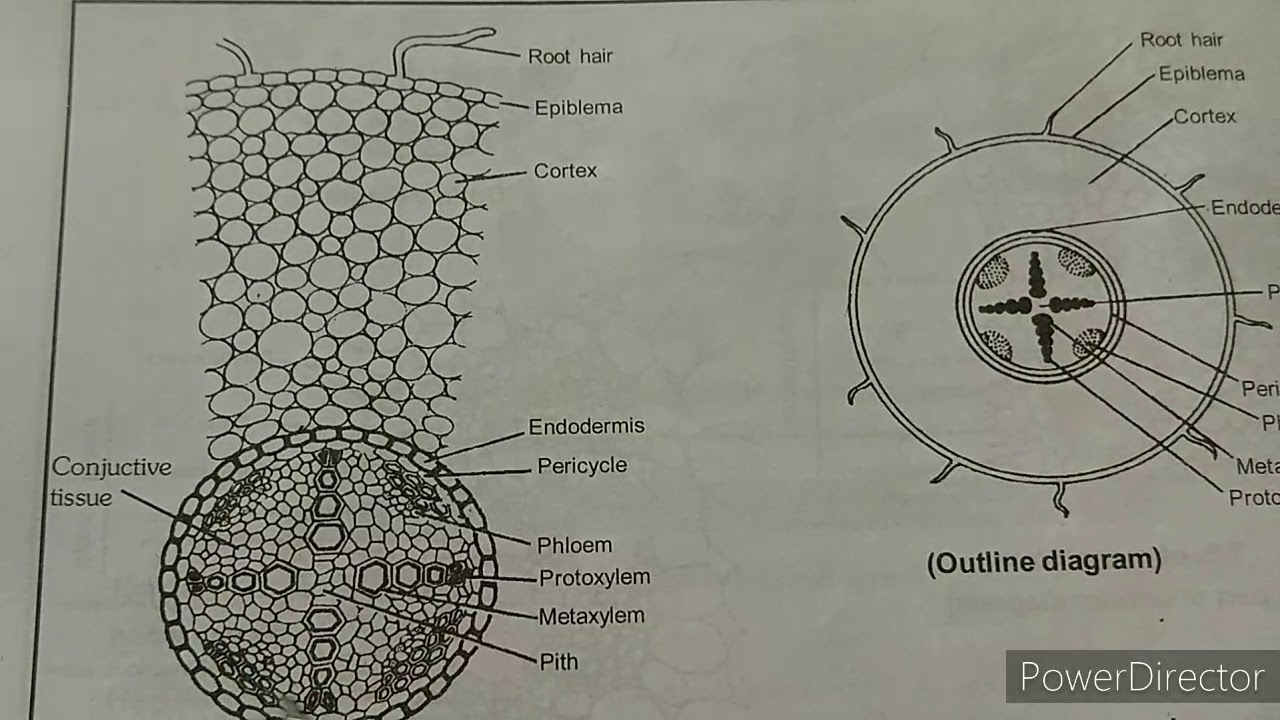
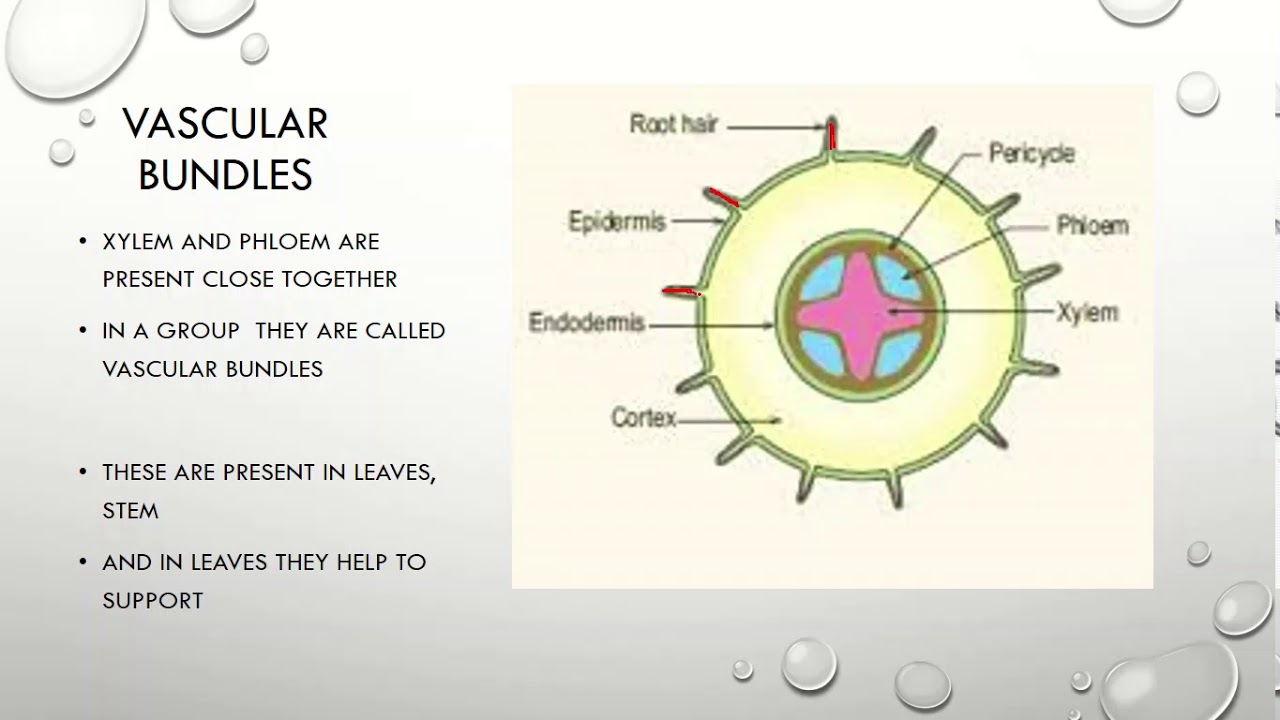
a). Hypodermis b). Outer cortex c). Inner cortex d). Endodermis (3). Stele a). Pericycle b). Vascular bundles c). Medullary rays d). Pith (1). Epidermis Ø Epidermis is the outermost layer, composed of parenchymatous cells. Ø Usually, epidermis composed of single layer of cells. Ø Cells are closely packed without any intercellular spaces.

Identify the vascular bundles given in the following figures . Sarthaks eConnect Largest
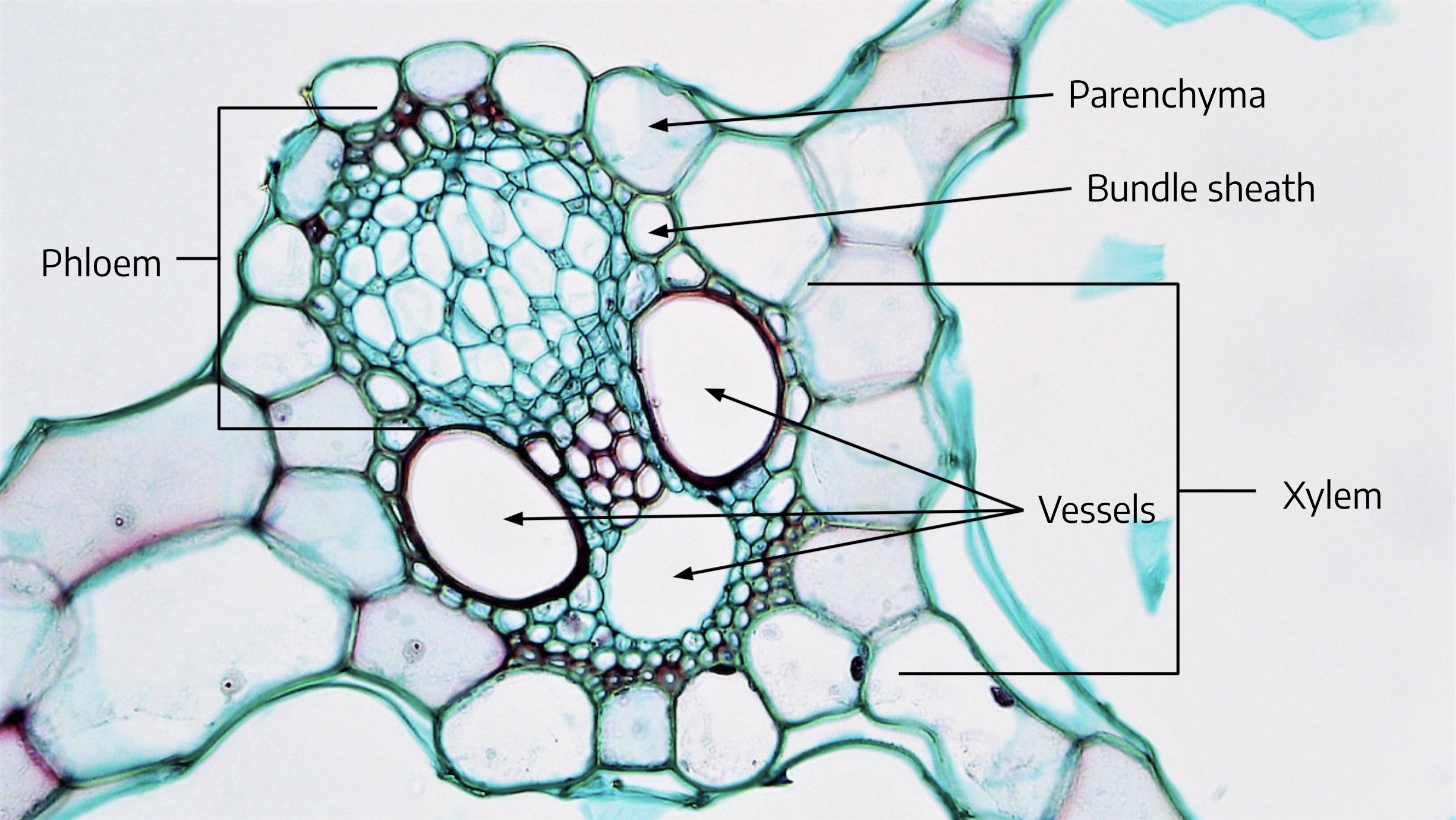
The Vascular bundle is a strand of special vascular tissue in plants. It consists of two complex tissues, xylem and phloem. Vascular bundles are one of the major components of the vascular tissue system in plants. What are Vascular Bundles?

Tissue System in Plants Types of tissue system Embibe
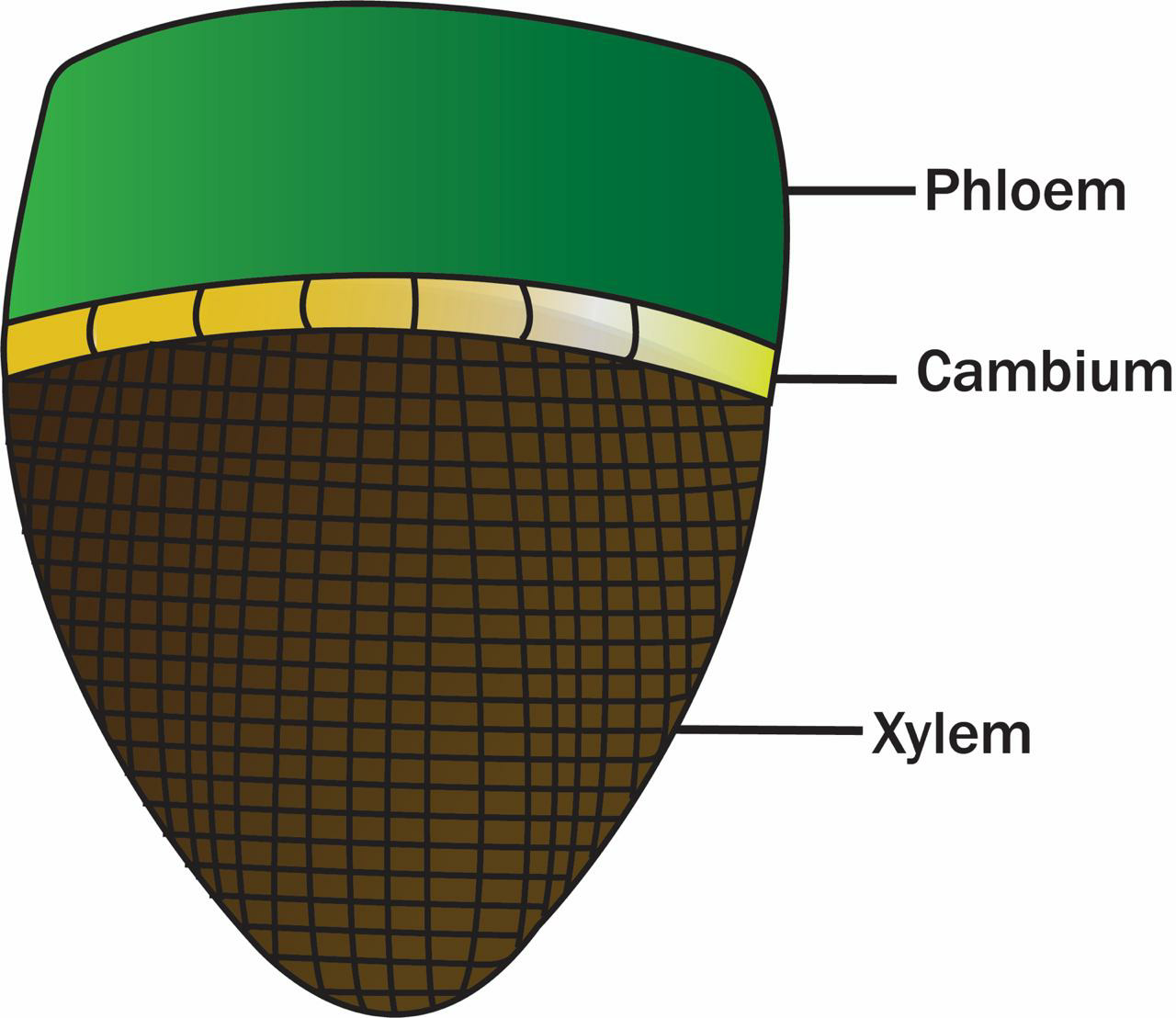
Image by RolfDieterMueller ( CC-BY) Figure 3.3.2.3 3.3.2. 3: In eusteles (left), vascular bundles are arranged around the periphery of the ground tissue. The xylem tissue is located toward the interior of the vascular bundle, and phloem is located toward the exterior. Primary phloem fibers cap the vascular bundles.

Stem Growth Biology for Majors II
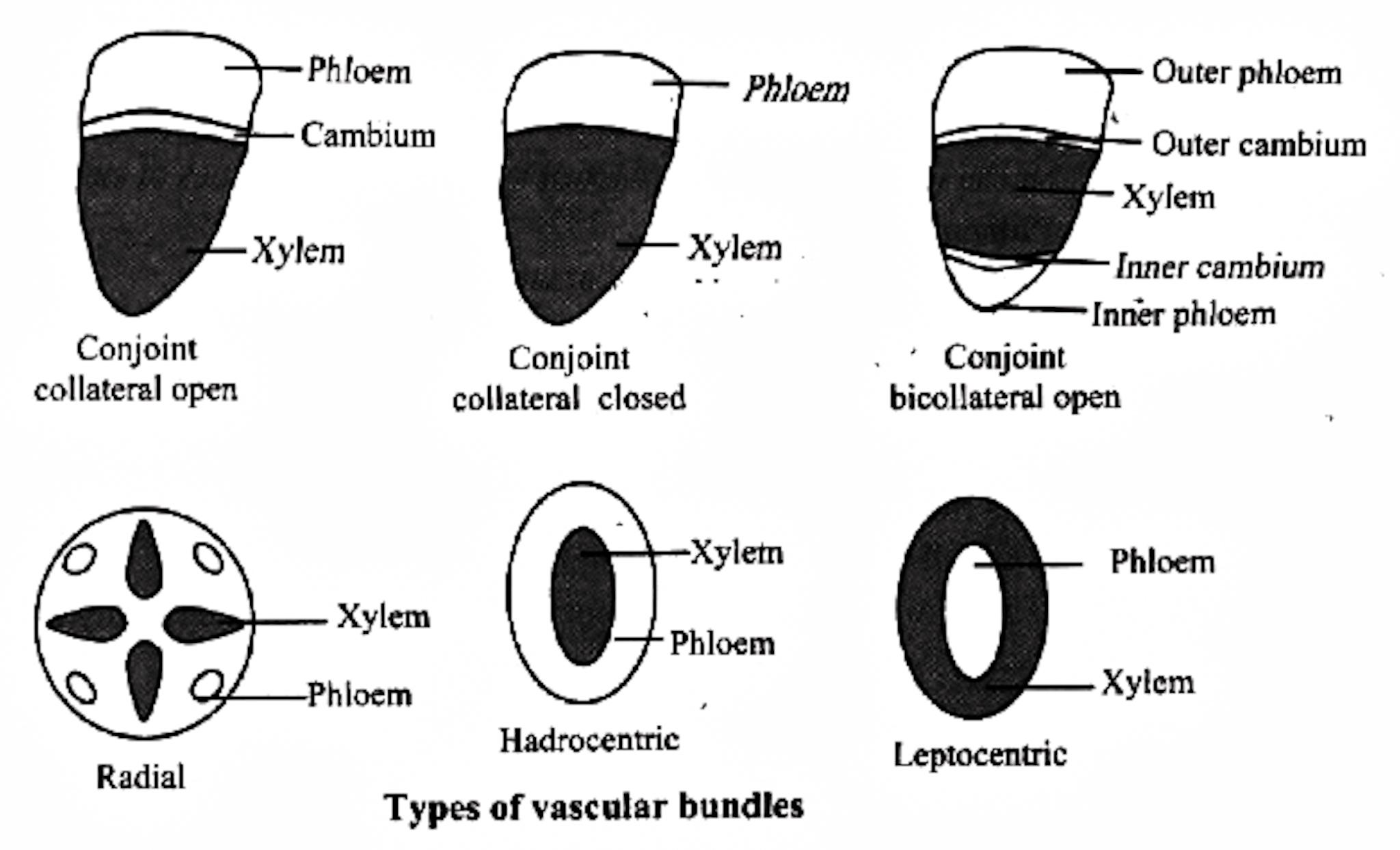
A group of xylem and phloem forms a vascular bundle. The different types of vascular bundles met within plants are: 1. Radial bundles (Simple): Xylem and phloem are seen as patches and they alternate each other, and occupy the different radii on the axis separated by non conductive tissue. example: Dicot and monocot roots. 2.
PPT Vascular bundles PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1710731
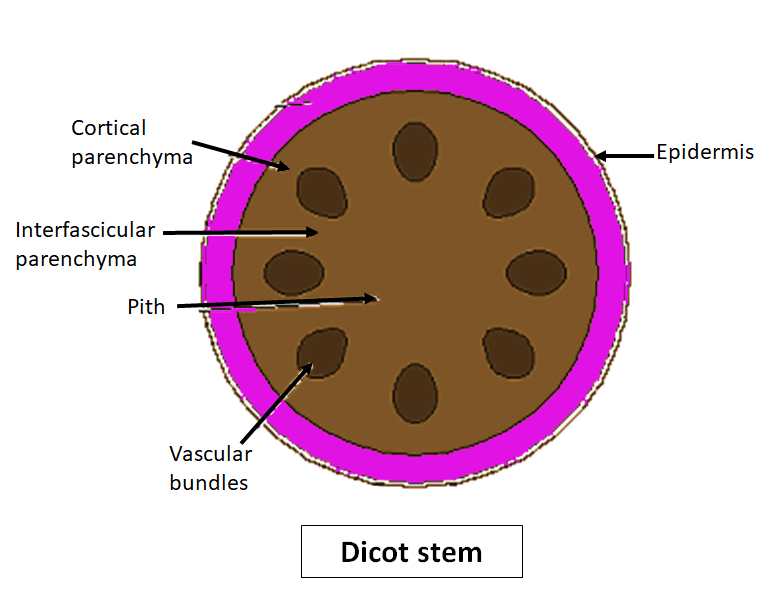
Since there is no ring of vascular bundles, there is no "inside" pith and "outside" cortex. All the ground tissue is considered to be cortex. Monocot corn stem cross section showing vascular bundles. Melissa Ha. CC BY-NC 2.0. In monocot vascular bundles the phloem is always oriented toward the outside of the plant and the xylem toward.
What Is Vascular Bundle Hindi Best Design Idea
Open vascular bundles are the characteristic of dicotyledons (dicots). The cambium present between xylem and phloem is called FASCICULAR CAMBIUM. In closed vascular bundles, the cambium will be absent (fascicular cambium absent) and they do not show secondary growth (closed for secondary growth).
Solved What morphology is evident the vascular bundle shown
As leaf traces connect the vascular bundle system of the trunk with the vascular bundles of the petioles, cross-sections from the cortical zone of the trunk and from a petiole were also stained (Fig. 7b and c). In leaf traces of the outer cortical zone of the trunk, a second fibre cap seemed to develop on the xylem side of the vascular bundles as fibre cells were seen on this side, opposite to.
What Is Vascular Bundle And Its Types Best Design Idea
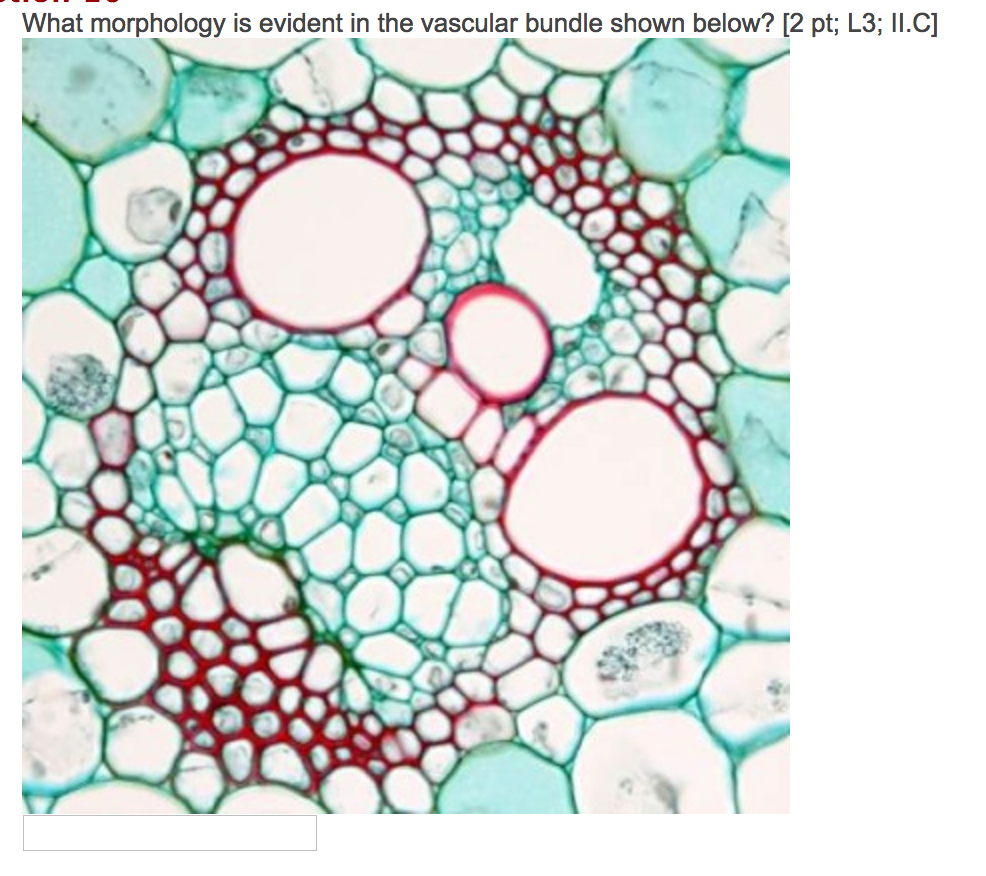
In the larger vascular bundle, it is easier to distinguish the large, open vessel elements (stained red). Within the vascular bundle, the xylem tissue is closer to the upper epidermis and the phloem tissue is closer to the lower. Each vascular bundle is surrounded by larger cells with darkly-stained contents. These make up the bundle sheath.

Anatomy of the vascular bundles. LM images of cross sections taken... Download Scientific Diagram
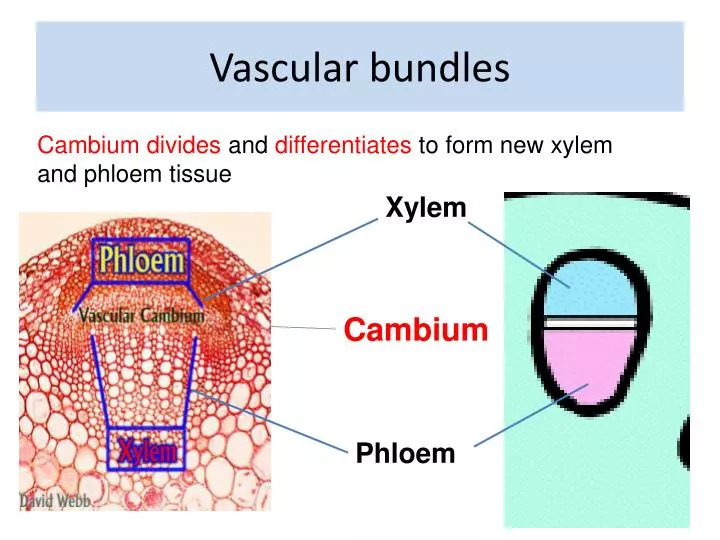
A layer of cells called cambium is sometimes present between xylem and phloem, referred to as an open vascular bundle, e.g, dicot stem. In closed vascular bundles, there are no cambial cells present between the xylem and phloem, e.g, monocot stem. Bicollateral Bundles
class 11th Anatomical structure of root and Vascular tissue system 02 06 2020 YouTube
Download scientific diagram | Schematic diagram for measuring the radial length/tangential diameter of an open vascular bundle in F. yunnanensis culm. M: metaxylem, P: phloem, Px: protoxylem, R.

Define open vascular bundle
1. Vascular bundle contains a strip of cambium in between phloem and xylem. 2. Phloem and xylem do not lie in direct contact with each other. ADVERTISEMENTS: 3. Due to activity of cambium, original or primary phloem and xylem move away from each other. Secondary phloem and secondary xylem are formed in between. 4.
Radial vascular bundles occur inA. StemB. Monocot rootC. Dicot rootD. Both monocot and dicot roots
There are open vascular bundles when a vascular cambium layer (in dicots) is present. Those devoid of it (in monocots) are closed vascular bundles. Thus, vascular bundles typically represent the organization of xylem and phloem and their association with other accessory transporting tissues.

SOLVED Draw and label the structure of open vascular bundle.
Vascular bundle; Answer . The diagram shows a cross section of a dicot stem, and we need to identify one of the structures in it. To do this, let's look at the different structures in a dicot stem and their functions. The epidermis is a single layer of cells that forms the outer covering of the plant stem..
The Vascular System Scientific Publishing
Solution Verified by Toppr An open vascular bundle is characterized by the presence of cambial ring between the xylem and phloem bundles. These are seen in dicot stem which undergoes secondary. The diagram represents the open vascular bundle. Solve any question of Anatomy Of Flowering Plants with:- Patterns of problems > Was this answer helpful? 0
Department of Botany
Bamboos have a hierarchical gradient structure, that is, a macroscopic gradient structure in culm diameter and a microscopic one in the bundle sheath distribution [1-4].A bamboo culm is made up of two kinds of cells, matrix tissue cells (parenchymatous) and sclerenchyma cells (vascular bundle) [5, 6].Vascular bundles made up of sclerenchyma cells act as reinforcement in bamboo.
Vascular bundles in root and stem YouTube
phloem together constitute vascular bundles (Figure 6.2). In dicotyledonous stems, cambium is present between phloem and xylem. Such vascular bundles because of the presence of cambium possess the ability to form secondary xylem and phloem tissues, and hence are called open vascular bundles. In the monocotyledons, the vascular bundles have no